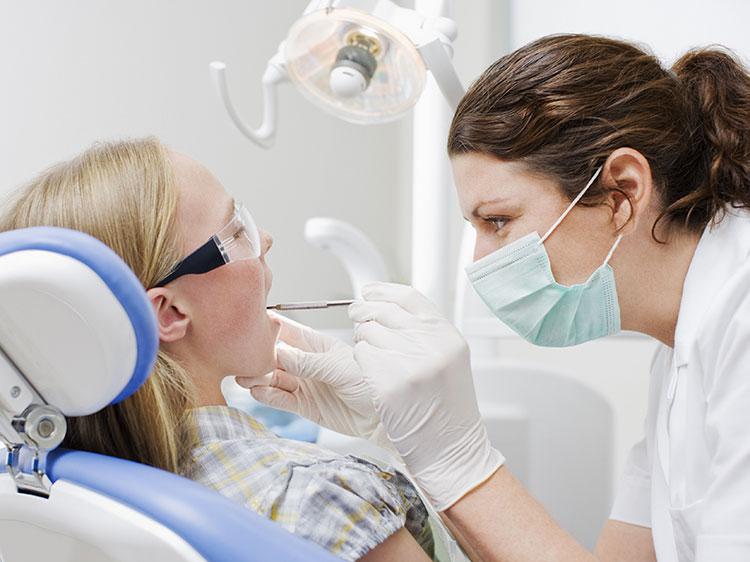
HIV confirmation testing plays an important role in diagnosing HIV infection. The initial antibody-antigen screening test is not a definitive test for HIV infection, so confirmatory testing is required. In some cases, the same test sample can be used both for the initial screening test or the HIV differentiation. In other cases, a second sample must be taken.
p24 antigen neutralization assay
For HIV confirmation, the p24 antibody neutralization test is used. This test reports the results as reactive or not-reactive based upon a pre-determined cutoff. To confirm the results, duplicate samples are taken. If the initial test's result is negative, the patient will be deemed infected. This test also has a negative component.

HIV RNA testing
HIV RNA testing for HIV confirmation testing detects HIV in most people within 1-4 week after infection. It may take up three weeks for HIV RNA to be detected in some individuals. HIV testing should always be done as soon before possible HIV exposure.
ELISA test
The ELISA test for HIV confirmation uses a dye to detect antibodies to HIV. The liquid changes in colour when the marker antibodies are present. When they are absent, the liquid remains clear. If a sample is coloured, it indicates that the individual has been infected. A clear sample is an indication that the person is healthy. The first two generations of the ELISA test look for the antibody alone while the third and fourth generation look for the antibody and antigens.
NAT Test
For HIV confirmation and monitoring viral loads in chronically ill persons, the NAT is used. This test can detect HIV as low as 20 copies per milliliter. This test is routinely used in clinical practice.
RT-PCR Test
The RTPCR test for HIV confirmation detects HIV RNA. To extract the viral RNA, it requires special operating environments and techniques. It is more sensitive, specific and reliable than other HIV tests.

Viral load test
For HIV positive people, the routine viral load test is done by health care providers. It should be checked at least yearly, and more often if you are having any symptoms of HIV infection. Viral load is important because it shows if you have a high or low amount of the virus in your blood. High viral loads can cause rapid loss of CD4 cells and HIV disease. But, it is possible for the viral load to fluctuate and not be a concern.
FAQ
What does the "health care” term mean?
Health care refers to delivering services related to maintaining good physical and mental health.
What about the role of the private sector?
In delivering healthcare, the private sector is vital. It also provides equipment used in hospitals.
It also covers some hospital staff. So it makes sense for them to take part in running the system.
However, there are limitations to what they can offer.
It is not always possible for private providers to compete with government services.
And they shouldn’t try to run it all. This could lead to a system that doesn't provide good value for money.
What is an infectious disease?
Infectious disease can be caused by germs (bacteria or viruses) Infectious diseases can spread quickly by close contact. You can get measles or mumps, rubella (German whooping cough), pertussis/whooping chives, rubella ("German measles"), measles), pertussis ("whooping cough"), rubella ("German measles"), chickenpox), strep thyme), hepatitis A/B, HIV/AIDS), herpes simplex viruses, syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia
Statistics
- Price Increases, Aging Push Sector To 20 Percent Of Economy". (en.wikipedia.org)
- Over the first twenty-five years of this transformation, government contributions to healthcare expenditures have dropped from 36% to 15%, with the burden of managing this decrease falling largely on patients. (en.wikipedia.org)
- The health share of the Gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to continue its upward trend, reaching 19.9 percent of GDP by 2025. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Healthcare Occupations PRINTER-FRIENDLY Employment in healthcare occupations is projected to grow 16 percent from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding about 2.6 million new jobs. (bls.gov)
- Consuming over 10 percent of [3] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
What are the 4 Health Systems
The healthcare system includes hospitals, clinics. Insurance providers. Government agencies. Public health officials.
The goal of this infographic was to provide information to people interested in understanding the US health care system.
These are some of the most important points.
-
Healthcare spending is $2 trillion annually, representing 17% of the GDP. This is nearly twice the amount of the entire defense spending budget.
-
Medical inflation reached 6.6% for 2015, more than any other category.
-
Americans spend 9% on average for their health expenses.
-
There were more than 300 million Americans without insurance as of 2014.
-
Although the Affordable Care Act (ACA), has been passed into law, it is not yet fully implemented. There are still significant gaps in coverage.
-
The majority of Americans think that the ACA needs to be improved.
-
The US spends the most money on healthcare in the world than any other country.
-
Affordable healthcare would mean that every American has access to it. The annual cost would be $2.8 trillion.
-
Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance cover 56%.
-
The top 3 reasons why people don't get insured include not being able to afford it ($25 billion), not having enough time to look for insurance ($16.4 billion), and not knowing about it ($14.7 billion).
-
There are two types, HMO (health maintenance organization), and PPO (preferred providers organization).
-
Private insurance covers almost all services, including prescriptions and physical therapy.
-
Public programs cover hospitalization, outpatient surgery, nursing homes, hospice care, long-term care, and preventive care.
-
Medicare, a federal program, provides seniors with health insurance. It pays for hospital stays and skilled nursing facility stays.
-
Medicaid is a joint state-federal program that provides financial assistance to low-income individuals and families who make too much to qualify for other benefits.